NARRATION:When we say sequencing, what do we mean? Well, in everyday terms we mean the correct order in which something should happen. So, let’s talk about putting your socks and shoes on. There is a right way and a wrong way to do this, and the order - or sequence - is important. I mean, you wouldn’t try and put your shoes on then try and put your socks on, would you? Because frankly, that just ain’t going to work.
The more complicated the task, the more important the sequence becomes. We also need to make sure those instructions have all the right details. It’s like me asking someone to assemble my perfect sandwich and them putting in all the wrong ingredients in the wrong order, and it ends up looking like this tragic looking effort here. I would need to give them a detailed sequence of instructions so that I don’t end up with that. With food we call that list a recipe. So here it goes…
First, take the bread roll and slice it down the middle… nooo, not that way! Rewind… take the bread roll and slice it horizontally across, yes like that. Now, take the lid off the butter and take a knife and scrape some of the butter onto the inside of the bread bun… excellent. Now for the lettuce and some tomatoes… add the lettuce to the bottom of the bread bun… no, not underneath it. On top of it… seriously! Anyway, you get the picture. If you don’t do everything in the correct order and with all the right details then the end result won’t be what you want.
Let’s think about how this works with computers. We call the list of instructions for a computer a program, rather than a recipe. But the idea is the same. The problem is, computers don’t know when they have been given the wrong instructions, or if the steps are in the wrong sequence. It just goes on following the program anyway. When we carry out a task we can use our initiative to fix problems as they come along.
Imagine a computer program that tells the robotic machines in a fizzy drink factory how to fill up the bottles on the conveyor belt. If the instruction sequence in the program isn’t in the correct order, and it puts the lids on before it fills up the bottles, then we would not only be left with empty bottles but a whole lot of cleaning up! So, we can see that sequencing is an important part of writing useful computer programs that help computer-controlled devices to do the jobs we planned.
Writing programs for your own computer games is a good way to practice your sequencing skills and get everything in the right order. This game needs you to get the mini-me to jump over the zombie piranhas and walk across the bridge to the other side. Now, if I wrote the program with the steps out of sequence, and I asked it to walk first then jump, then I'd end up gobbled up by the zombie piranhas!
It is the same principle when we look at the incredible computerised robots that build cars. These robots carry out thousands of movements and tasks to build each car, and everything needs to be precise and in sequence. It’s a bit like dancers working together on a complicated dance sequence, everyone needs to know their moves and everyone needs to perform them in the correct order.
And if we think even bigger than that, then just imagine how precise the sequencing needs to be in the hundreds of different computer programs that control a rocket launch. There can’t be any errors in all those instructions, everything needs to be in the right order and with all the right details. This means the programs must be tried and tested over and over again to make sure everything works as planned.
The power of getting things in exactly the right order is absolutely crucial when writing computer programs, so it’s clear to see just how important sequencing is when it comes to computers and also ourselves. After all, nobody wants wet socks!
Video summary
This short film covers the concept of sequencing, or making sure things are in the right order, and explores what might happen if things are done in the wrong order, or sequence.
The film starts with some real world examples, including getting dressed and making a sandwich, and explores what might happen if things are done in the wrong order, or sequence.
It also looks at how instructions need to be precise and unambiguous.
The film then expands this idea into the more complex real world example of an automated factory, and then a simple program for a computer game.
It also looks at the importance of sequencing in the computer programs behind larger applications, like air traffic control systems.
This short film is from the ¬ť∂Ļ‘ľŇń Teach series, Cracking Computing.
Teaching Notes
The importance of sequencing instructions accurately in computer programs can be explored initially using practical activities and games where instructions are given and the outcome depends on the quality of those instructions.
Pupils could pretend to be robots waiting for instructions and follow them precisely to complete a simple task. This might work well as part of a PE lesson, using simple hall apparatus to create an obstacle course that must be navigated by the ‚Äėrobot‚Äô under instruction from a team of ‚Äėprogrammers‚Äô.
It is important that pupils are clear about their intention for the outcome of the sequence of instructions (the algorithm). This will allow them to see mistakes and correct them, or debug.
Floor robots and other physical systems or simulations can be useful when starting work on sequencing as the outcome of each part of the sequence is visually obvious. This makes debugging a natural part of the activity.
Other subjects
English: Sequencing fits into several areas of non-fiction writing, including instructions and explanations of a process. Comparisons can be made between these kinds of texts and simple computer programs and algorithms.
Maths: Creating and solving number sequence puzzles would work well to support this concept and introduce the idea of rules governing the way the sequence progresses. For example, ‚Äúadd five‚ÄĚ or ‚Äúmultiply by two and then add four‚ÄĚ, etc.
This short film is suitable for teaching:
- KS2 computing curriculum in England
- Technologies curriculum area at 2nd Level in Scotland
- KS2 digital competence framework in Wales
- KS2 using ICT cross-curricular skill in Northern Ireland
Algorithms. video
This short film for primary schools outlines how algorithms are sets of instructions to make something happen, before explaining further using a recipe analogy.

Computer networks. video
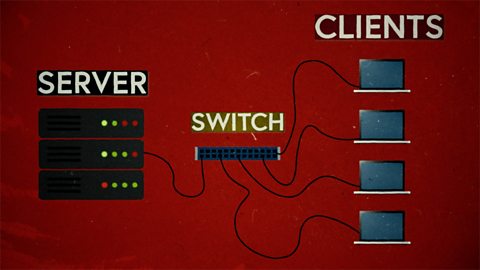
This short film explains computer networks. It looks at different types of computer network and the elements that make up a basic network including clients, servers, switches and hubs.
Creating with computing. video
This short film explores the many creative computing tools we have access to, with a focus on how they are used to create new creative content and media.

Debugging. video
This short film uses computer games to explain debugging, which is the process of finding and correcting errors in computer programs.

Decomposition. video
This short film explains how decomposition involves breaking one big problem down into smaller, more manageable problems that can be tackled step by step.

Input and output. video
This short film gives a brief history of input and output methods with examples, and brings us up to date with examples of familiar input and output devices that we use every day.

Logical reasoning. video
This short film outlines logical reasoning as ‚Äėsensible thinking‚Äô when following rules, and explains how a problem with a computer program can be solved using logical reasoning.

Repetition. video
This short film for primary schools explains how repetition within computing allows a command to be repeated to make a computer program more efficient.

Search technologies. video
This short film gives a brief history of the development of the internet and the invention of the world wide web by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, and explains the role of a search engine.

Selection. video
This short film covers the use of selection in simple computer programs, and shows how this idea of yes/no questions can allow computers to respond to external conditions and select different paths.

Variables. video
This short film explores how computers use variables to store things that change, like names, numbers and scores.

Working with data. video
This short film explores how data is collected using digital devices in response to questions, and how it is organised into tables, records and fields on a computer system.
