Chemical reactions
Introduction to chemical reactions
Chemical reactions make new chemicals. Atoms are rearranged during a chemical reaction, but the number of atoms does not change.

Oxidation
In an oxidation reaction, a substance gains oxygen atoms. Learn more in this KS3 Chemistry guide from Bitesize.

Catalysts
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction. Catalysts are useful because they do not get used up during a reaction.

Exothermic and endothermic reactions
Exothermic reactions release energy into the surroundings, so they usually feel hot. Endothermic reactions are the opposite.

Writing word equations
Chemical reactions can be represented by word equations. Learn more in this KS3 Chemistry guide from Bitesize.

Writing symbol equations
Chemical reactions can be summarised using symbol equations. Learn more in this KS3 Chemistry guide from Bitesize.

Conservation of mass
During chemical reactions or a change of state, no atoms are created or destroyed. The total mass of chemicals before and after a reaction remains the same.

What is combustion?
Combustion is another name for burning. In a combustion reaction, fuel is burned and reacts with oxygen to release energy.

Thermal decomposition
Thermal means heat. Decomposing is the process of breaking down. Thermal decomposition is a chemical reaction that happens when a compound breaks down when heated.

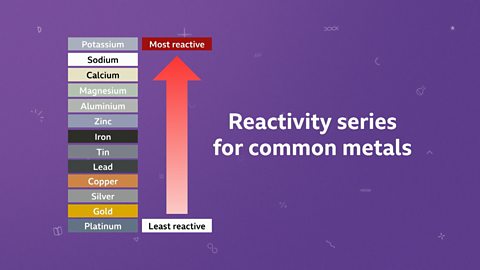
Introduction to displacement reactions
In a displacement reaction, a more reactive element replaces a less reactive element from its compound.
How to make COâ‚‚
A simple, step-by-step, visual guide showing you how to make COâ‚‚.

How to make bread
A simple, step-by-step, visual guide showing you how to bake bread.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription