Key points
- Most fruits have seeds, which make them capable of developing into new plants.
- A fruit is a matured and ripened ovary of a plant, which is why it contains seeds for plant reproduction.
- Seeds are dispersed in a variety of ways.
What is fertilisation?
Fertilisation is the joining of gameteSex cells. In plants the male sex cell is pollen and the female sex cell is an ovule..
- Pollen is the male sex cell in a plant.
- Pollen grains land on the stigmaThe top of the female part of the flower which collects pollen grains. with the help of the wind, water, insects or animals.
- A pollen tube then grows down through the style to the ovary.
- The nucleus from the male sex cell then moves down the tube to join with a female sex cell (an ovule) in the ovary.
- Fertilisation is when the two nucleiPlural of nucleus. Part of cells which contains the genetic material in the form of DNA. join.
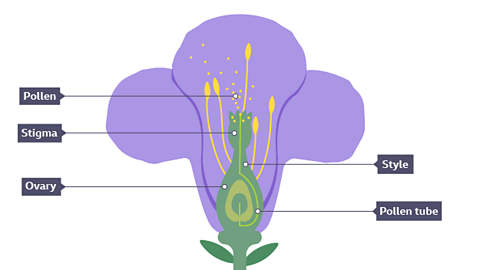
Image caption, A pollen grain is transferred from one flower to another. A pollen tube grows from the stigma to the ovary.
Image caption, The nucleus of the pollen grain passes through the pollen tube and joins with the egg cell inside an ovule in the ovary.
Image caption, The fertilised ovule will develop into a seed.
1 of 3
Fruit and seed formation
Fruit comes from flowering plants, and it is grown in the following process:
- The ovary develops into a fruit.
- The ovary wall becomes the rest of the fruit.
- Each fertilised ovule forms a seed.
Parts of the seed
A seed has three main parts:
- Embryo: the young root and shoot that will become the adult plant
- Food store: starch for the young plant to use until it is able to carry out photosynthesis
- Seed coat: a tough protective outer covering
Germination
Contents of the ovule become the food source for when the plant starts to grow or germinateThe process controlled by enzymes in which the seed begins to develop into a new young plant.. The seeds will often lie dormant until the conditions around it are just right for germination. Factors such as temperature, concentration of oxygen in the air and water will affect germination.
Seed dispersal

Seed dispersal is the transport of seeds from the plant to another area in order to grow.
These are the main ways in which seeds can be dispersed:
- Animals
- Explosion
- Wind
- Water
Seeds must be dispersed or spread away from each other and from their parent plant. This is to reduce competition between one another and increase their chances of survival.
Plants compete with each other for resources including:
- Light
- Water
- Space
- Minerals in the soil

| Dispersal method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Animal (exterior) | Some plants use hooks on their fruits. These attach themselves to the fur of mammals or feathers of birds and get carried from one place to another. | Cocklebur, goose grass, burdock |
| Animal (interior) | Fleshy fruits are eaten by animals. The seeds are then dispersed after passing through the digestive system of animals that have eaten the fleshy fruits. | Tomato, raspberry, grape |
| Animal (burial) | Hard nuts are usually destroyed if chewed or eaten. However, animals such as squirrels may store them to eat later and forget to go back to get them, giving them a chance to germinate. | Acorns |
| Explosion/self-propelled | Have a pod that bursts open when ripe, throwing the seeds away | Pea pod |
| Wind | Some plants have seeds that act as parachutes, which are carried away by the wind | Dandelions |
| Wind (spinning) | Some seeds are winged. They spin like helicopters as they fall from the tree, providing a longer time for dispersal by wind. | Maple fruits, sycamore |
| Water | Some plants grow near rivers, lakes, streams or oceans. Their fruits or seeds fall from the plant and are carried away by the water. | Coconut, silver birch, willow |
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Test questions
What are the four main ways seeds are dispersed?
- Animal - interior, exterior, burial
- Explosion/self-propelled
- Wind
- Water
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Reproduction
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 5

- count2 of 5
- count4 of 5
