Key points
- The skeleton is made up of more than 200 bones.
- Biomechanics is the study of how the skeleton moves at its jointPart of the body which allows movement including the neck, elbows, hips and knees. when muscles exert force on bones.
Video
Look at that kick! To make a big shot like that, the body has to do an extraordinary number of little things.
The study of how your body does all of that is called biomechanics. Whether it's kicking a ball, throwing a dart or leaping over hurdles, it's all made possible by bones, muscles and joints. That's why biomechanics is used in all your favourite sports. Studying this relationship can improve performance and give athletes the edge.
Look at how the femur, fibula and tibia are attached to the hamstrings and how the quadriceps work together to exert force over the knee joint to make it move.
This happens with joints all over the body to help with vital movements. The humerus radius and ulna are attached to the biceps and triceps, which work together to exert force over the elbow joint to make it move.
Unfortunately biomechanics only applies if you have muscles, joints and bones. Sorry pal.
Can you answer these questions based on the video?
1. Name the three bones in your leg.
2. Which two muscles move these bones?
- Femur, fibula and tibia
- Hamstring and quadriceps
Joints
The most common type of joint in your body are synovial joints. These have the widest range of movement. Examples include hinge joints, pivot joints and ball and socket joints.
Bones are very strong but will eventually wear away if they touch. To stop this happening there is cartilageA tough, flexible material found in the nose and ears, but also between bones in your spine, knees and around your trachea. between them. This is a tough but smooth tissue found at the ends of bones which reduces friction when they rub together. To help reduce this further a liquid called synovial fluid surrounds the ends of the bones.
ligamentA strong cord-like tissue which connects bones on either side of joints together. are strong cord-like tissues which attach to the ends of bones either side of the joint. They hold the bones in the correct place. tendonA strong cord-like tissue which connects muscles to bones. are also strong cord-like tissues but these attach the bones in the joint to muscles which contract and relaxMuscles get shorter by contracting and return to their original length when they relax. Muscles pull on bones for movement. to move them.

Athletes occasionally damage their tendons or ligaments when they twist joints beyond their normal range. Repeated stress on joints can eventually wear away the cartilage causing bones to rub together. This often happens in older people and causes pain.

Hinge joints: elbow and knee
The elbows are hinge joints. These act like the hinges on a door and only allow movement in two directions. Elbows allow the movement of the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the lower arm to pivot.
The knee is a hinge joint which allows the femur bone in the thigh and the fibula and tibia in the lower leg to move. Unlike the elbow, knees also allow some rotation. Fingers also have hinge joints.
Pivot joints: lower arm and neck
The radius and ulna in the lower arm allow the elbow to hinge. However, these bones are also joined together in a pivot joint. This means they can rotate around each other. To see this stretch your arm and hand out then turn your hand palm face up then face down. There is another pivot joint in the neck.
Ball and socket joints: hip and shoulder
The hips are ball and socket joints. These allow the greatest amount of movement. At the top end of the humerus bone in the upper arm is a ball shape. This sits in a depression in the shoulder blade (scapula bone) which allows it to rotate. The same is true at the top end of the femur bone which sits within a depression of the pelvic bone in the hip.
Antagonistic muscles
Muscles can only pull and cannot push. This would be a problem if the joints were controlled by just one muscle. As soon as the muscle had contracted and pulled on a bone, that would be it, with no way to move the bone back again. This problem is solved by having muscles in pairs, called antagonistic musclesA pair of muscles that act on a joint. As one muscle contracts the other relaxes.
For example, the elbow joint has two muscles that move the forearm up or down. These are the biceps on the front of the upper arm and the triceps on the back of the upper arm:
- to raise the forearm, the biceps contracts and the triceps relaxes
- to lower the forearm, the triceps contracts and the biceps relaxes
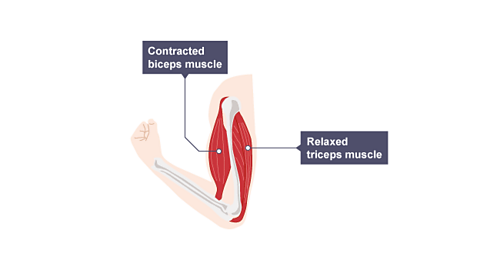
Image caption, The biceps contracts and raises the forearm as the triceps relaxes
Image caption, The triceps contracts and lowers the forearm as the biceps relaxes
1 of 2
Forces exerted by muscles

Many of the muscles in the body are different shapes and sizes and cause movement of bones in different directions. It is therefore difficult to compare which muscle applies the biggest force for its size.
The jaw muscle possibly applies the greatest force. Without this joint food couldn't be eaten!
The turning effect of a force is called a momentThe turning effect of a force.. Moments are calculated by multiplying the force applied by the distance from the pivot.

Test your knowledge
Quiz
Test questions
What are the three main types of joints in the human body?
- Hinge joints
- Pivot joints
- Ball and socket joints
Write a paragraph to answer the following question. Tap 'Show answer' to see three points you could have included.
Describe how muscles work together to move bones.
- Muscles can only pull and cannot push.
- Muscles come in antagonistic pairs.
- When one muscle in a pair contracts the other relaxes, when the second muscle then contracts the first one relaxes.
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Living organisms
Find out more by working through a topic
- count8 of 15
- count9 of 15

- count10 of 15

- count11 of 15