Key points
When energyEnergy can be stored and transferred. Energy is a conserved quantity. is stored within a systemAn object or group of objects that interact., equations can be used to quantify how much is stored.
Energy is conserved. It cannot be created or destroyed. Energy can be transferred between stores.
The total energy has the same value before and after any changes.
The gravitational potential energy store
As an object is lifted, workThis is done when energy is transferred. is done against the force of gravity.
The higher the object, the more energy is in the gravitational potential energy store.
Energy in the gravitational potential energy store ( Ep)
Use the following equation to calculate how much energy is stored in the gravitational potential energyThe energy an object possesses due to its position above the ground.:
Energy in the gravitational potential energy store (Ep) = mass (m) x gravitational field strength (g) x height (h)
\(Ep = m \times g \times h\)
The unit of measurement for energy in the gravitational potential energy store is the joule (J).
On Earth, the gravitational field strength The force that attracts one kilogram towards another massive object, like a planet. Gravitational field strength has the symbol g and it is measured in newtons per kilogram (N/kg). (g) is 9.8 N/kg.
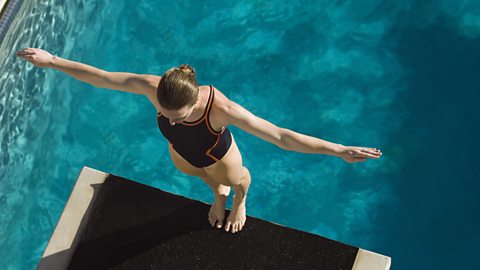
Example
A diving platform is 10 m above the ground. When an 80 kg diver climbs to the top of the platform, how much is the increase in energy in their gravitational potential energy store?
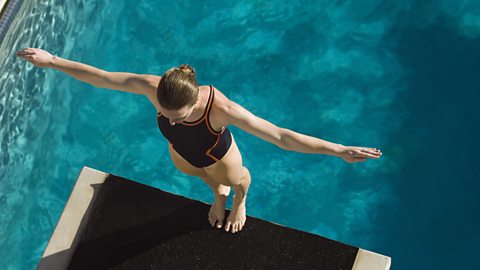
Energy in the gravitational potential energy store = ?
Mass = 80 kg
Gravitational field strength = 9.8 N/kg
Height = 10 m
use the following equation:
Energy in the gravitational potential energy store (Ep) = mass (m) x gravitational field strength (g) x height (h)
\(Ep = m \times g \times h\)
\(Ep = 80 \times 9.8 \times 10\)
\(Ep = 7~840~J\)
The kinetic energy store
The faster an object is travelling, the more energy there is in the kinetic energy store of the object.
How fast the object is moving is its speed. Speed is measured in m/s.
Velocity is speed in a particular direction. Velocity (v) is also measured in m/s.
The more mass an object has, the more energy in the kinetic energy store.
Energy in the kinetic energy store (Ek)
Use the following equation to calculate the amount of energy in the kinetic energy storeThere is more energy in the kinetic energy store if an object moves faster. of a moving object:
Energy in the kinetic energy store (Ek) = 0.5 x mass (m) x velocity² (v²)
\(Ek = 0.5 \times m \times v²\)
The unit of measurement for the amount of energy in the kinetic energy store is the joule (J).
Example
A runner with a mass of 60kg is running at a speed of 1 m/s. Calculate the amount of energy in their kinetic energy store.
Energy in kinetic energy store = ?
Mass = 60 kg
Velocity = 1 m/s
Use the following equation:
Energy in the kinetic energy store (Ek) = 0.5 x mass (m) x velocity² (v²)
\(Ek = 0.5 \times m \times v²\)
\(Ek = 0.5 \times 60 \times 1²\)
\(Ek = 0.5 \times 60 \times 1\)
\(Ek = 30~J\)
Test your knowledge
Quiz - Multiple choice
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Energy
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 6

- count6 of 6

- count1 of 6
- count2 of 6
