Viral diseases
virusAn ultramicroscopic infectious non-cellular organism that can replicate inside the cells of living hosts, with negative consequences. are not alive because they do not complete all of the seven life processes:
- movement
- respiration
- sensitivity
- nutrition
- excretion
- reproduction
- growth
We say 'strains' of virus and not species. Most are made of a relatively short length of the genetic material DNADeoxyribonucleic acid. The material inside the nucleus of cells, carrying the genetic information of a living being. which is surrounded by a protein coat.
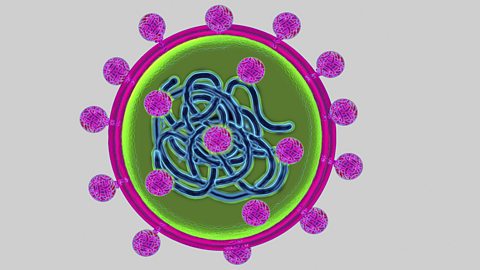
Viruses can often survive outside a hostThe organism lived on or in by a parasite. for long periods of time. When they have infected a suitable host cell or cells, they replicate themselves within the cell thousands of times. They do not divide and reproduce, but replicateTo create a copy or copies. their DNA and protein coats. These are then assembled into new virus particles. The host cell or cells then burst and other nearby cells can be infected with the virus. This process can be as quick as under one day for norovirusA common 'upset tummy' infection caused by a virus which is highly contagious. or several days for EbolaOften fatal disease caused by a virus which originated in Africa..
Viral infections cannot be treated by antibioticsSubstances that control the spread of bacteria in the body by killing them or stopping them reproducing..
Tobacco mosaic virus
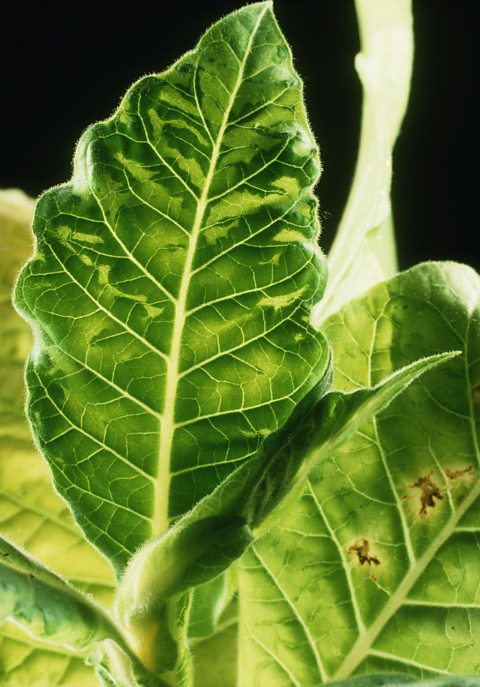

The tobacco mosaic virus infects tobacco and lots of other closely related species, such as tomatoes and peppers. It is transmitted by contact between plants, either naturally or through the hands of farmers. It infects the chloroplastContains the green pigment chlorophyll; the site of photosynthesis. of plant leaves and changes their colour from green to yellow or white in a mosaic pattern. It can also make leaves crinkle or curl up.
This reduces the plant's ability to photosynthesisA chemical process used by plants to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. Algae subsumed within plants and some bacteria are also photosynthetic. and grow properly, which reduces the crop yieldThe mass of a crop produced. for farmers.
There is no cure, therefore farmers must try to reduce the spread of the virus.
HIV/AIDS
HIVHuman Immunodeficiency Virus, a disease which damages cells in the immune system. stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This infection is transmitted by body fluids, often during unprotected sex, but also through cuts and injecting drugs using shared needles. Immediately after infection, people often suffer mild flu-like symptoms. These pass and for a period of time infected people might not know they are infected.
AIDSAcquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome – a disease of the human immune system caused by infection with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. Months or years after the infection of the HIV virus, it becomes active and starts to attack the person's immune systemThe body's defence system against entry of any foreign body, including pathogens and agents such as pollen grains. The role of the immune system is to prevent disease.. HIV at this point has become AIDS.
HIV is detected by screening patients for antibodyA protein produced by the immune system in humans (and other animals) that attacks foreign organisms (antigens) that get into the body. against proteins that are found on the virus. There is no cure for HIV /AIDS although many scientists are trying to find one. Currently, infected people are given antiviralsDrugs that prevent viruses replicating., which mean many people with the virus can live a long and healthy life.
Measles
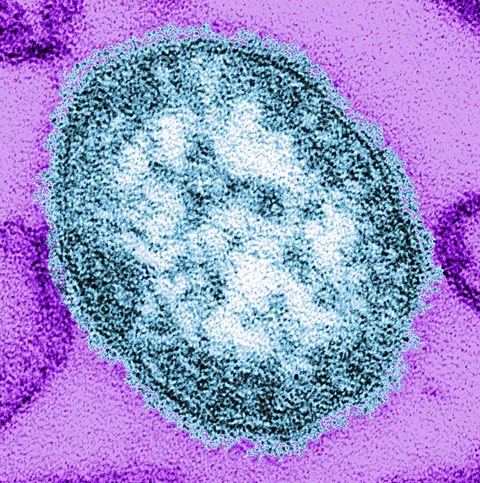
measlesAn infectious disease of the respiratory system caused by a virus. is a very infectious viral disease that is often caught by young children. It is transmitted through the air in tiny droplets after an infected person sneezes. It causes a fever and skin rash. Many children in developed countries are given vaccineSubstances containing disabled antigens of a particular disease, usually administered via injection. Vaccines stimulate the body to produce antibodies to provide immunity against that disease. against measles, but this is not the case throughout the world. Infection can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening complications in some people.
More guides on this topic
- Field investigations - OCR Gateway
- Monitoring and maintaining the environment - OCR Gateway
- Feeding the human race - OCR Gateway
- Treating, curing and preventing disease - OCR Gateway
- Cancer and cardiovascular disease - non-communicable - OCR Gateway
- Monitoring and maintaining health - non-communicable - OCR Gateway