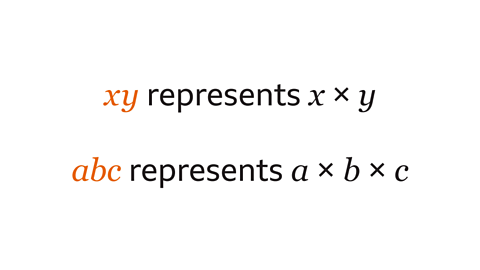Formulas and expressions
Real life situations can be represented by algebraic expressions and formula. We can then use these to solve problems such as working out costs, timings, quantities etc.
Forming expressions
Example
The length of a piece of wire is \(L\)centimetres.
A second piece is 5cm longer.
Write an expression, in centimetres, for the length of the second piece.
Solution
If the length had been given as a number we would just add 5 on. We can do the same here.
Answer
Length of second piece is \(L + 5\) centimetres.
In questions like this, the units are often already on the answer line.
As the answer is an expression, there is no = sign. We do not know the value of \(L\) and we were not asked to find it in this question.
Example
The length of a plank of wood is \(W\) centimetres.
A second plank is twice that length.
Write an expression, in centimetres, for the length of the second plank.
Solution
If the length had been given as a number, you would just multiply by 2. We can do the same here
\(2 \times W = 2W\)
Answer
Length of second plank is \(2W\) centimetres.
Example
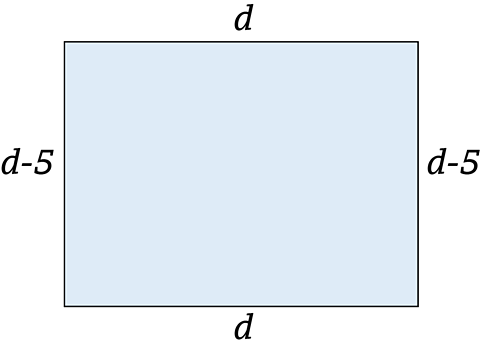
The length of a rectangle is \(d\) centimetres.
The width is 5cm shorter.
Write down and simplify an expression for the perimeter of the rectangle.
Solution
Width of the rectangle is 5cm shorter than the length.
\(width = d - 5cm\)
Perimeter is the distance right around the rectangle.
Adding all the distance starting at the top left hand corner gives:
\(Perimeter = d + d - 5 + d + d - 5\)
To simplify the expression, collect like terms.
\(d + d + d + d = 4d\)\(-5 -5 = -10\)
Put these terms together for the answer.
\( perimeter = 4d - 10\)

Formulae
A formulae is a general rule expressed in algebraic terms.
For example, to find the area of a triangle we use the rule:
half the base times the height
In algebraic terms, this is
\(A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h\) or more simply, \(A = \frac{1}{2}bh\)
where \(A\) stands for area, \(b\) stands for the length of the base and \(h\) for the height.
Example
Solution
Answer
The rule to calculate the perimeter of a rectangle is add the length and width and then multiply by 2
Write this as formula using \(P\) for perimeter, \(l\) for length and \(w\) for width.
Adding the length and width gives \(l + w\)
Multiplying by 2 gives \(2(l + w)\)
Writing the formula for the perimeter \(P = 2(l + w)\)
The bracket in the formula is important. Both \(l\) and \(w\) have to be multiplied by 2.Ěý
Ěý
\(P = 2l + 2w\) is also a correct formula.
Test yourself
Look at the leaflet promoting Jenny's business.
Write Jenny's total charge as a formula using \(C\) for charge and \(h\) for the number of hours.

Solution
Jenny charges ÂŁ24 per hour so for \(h\) hours she charges \(ÂŁ24 \times h\)
She also charges a ÂŁ50 call out fee, no matter how many hours she works.
Answer
\(C = 24h + 50\)
- The ÂŁ sign is not needed, it is assumed that the answer will be in pounds. Formulae do no usually contain units.
- \(C = 50 + 24h\) is also a correct formula. The order of the \(50\) and the \(24h\) does not matter.
Using Formulae
Formulae are rules which can be used to calculate everyday quantities such as costs, charges, times, areas, volumes etc.
To use a formula, numbers are substituted into the formula and the calculation is completed using those numbers.
Example
A local newspaper uses the formula below to calculate the charge for publishing advertisements.
\(C = 250 + 70w\)
where \(C\) is the charge in ÂŁs and \(w\) is the number of weeks the advertisement will appear.
Marcus wants to advertise his business for 8 weeks. How much will he be charged?
Solution
Substitute \(8\) into the formula instead of the number of weeks \(w\)
\(C = 250 + 70 \times 8\)\(= 250 + 560\)\(= 810\)
Answer
Cost = ÂŁ810
Don't forget to put the ÂŁ sign back in, although units are often already written on the answer line.
Test yourself
The formula \(F = 1.8C + 32\) can be used to convert temperatures from degrees Celsius (°C) to degrees Fahrenheit (°F).
The boiling point of water is 100°C. What is this in Fahrenheit?
Put 100 into the formula in place of C.
\(F = 1.8 \times 100 + 32\)\(= 180 + 32\)
Answer: 100°C = 212°F
Test yourself
More on M1: Algebra
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 7

- count2 of 7