Some things sink while other things float. Why is this? Let's find out!
Watch and learn
Video
How do things float? What forces are at work? Let's find out!
Title: Buoyancy
Some things float and other things don’t. If something can float, we say it is buoyant.
This penny coin weighs less than this toy boat. The boat is buoyant so it floats on the surface. The coin isn’t, so it sinks to the bottom.
Whether of not something will float is down to its density and shape.
Density is measurement that compares the mass, or amount of stuff in something, to its volume, or to how big it is.
This football is full of air. It floats in the water because it is less dense than the water.
This golf ball is filled with rubber. Rubber is much more dense than air or water so golf balls sink in water – as many golfers have found out.
Density and shape are important when designing and building boats. As long as the downward force of the boat on the water is not more than the upward force of the water, the boat will float.
Someone has been playing a trick with the weight of this toy duck. They’ve filled it with sand and made it more dense.
Shape is also important for buoyancy. The hulls of boats are designed to spread out as much area on to the water as possible. A hull with a big surface area means a boat will sit stable and high in the water by spreading the weight.
Try making a tinfoil boat. When does it sink, and why?
Floating and sinking

Whether and objects float or not is controlled by the Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. of the object.
Density is how tightly packed the material inside something is.
For example, a sponge ball and a marble have different density. You can feel the sponge ball is less dense because you can squeeze it and change its shape.
If you put them in water, the less dense sponge ball floats, and the more dense marble sinks.

What will happen if you place a hollow golf ball and a solid golf ball in a bowl of water?
The hollow ball floats. It is full of air which is less dense than water.
The solid ball sinks. That's because the material inside is tightly-packed and more dense than water.

If something has a density that is less than the density of the water, the object will float.
And if something has a density that is greater than the density of the water, the object will sink.
Buoyancy and forces
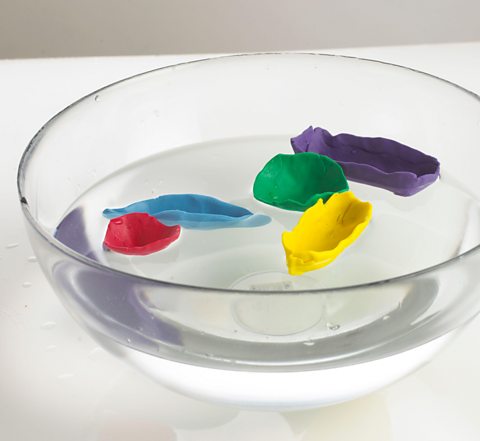

There are two forces acting on objects in water:
– the weight of the object being pulled down by gravity
- the upthrust from the water underneath the object pushing up.
If the object is less dense than water then the upthrust is greater than the weight and the object will float.
If the object is more dense than water the upthrust is less than the weight and the object will sink.
If an object floats we say that it is Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again..

What is buoyancy? revision-guideWhat is buoyancy?
Find out more about buoyancy.

Density and liquids
Did you know that liquids have different densities?
For example oil is less dense than water but syrup is more dense than water.
A less dense liquid will float on top of a denser liquid.
Also, salt water is denser than fresh water, so a ship will float higher in the salty sea than in the fresh water of a river.
Experiment
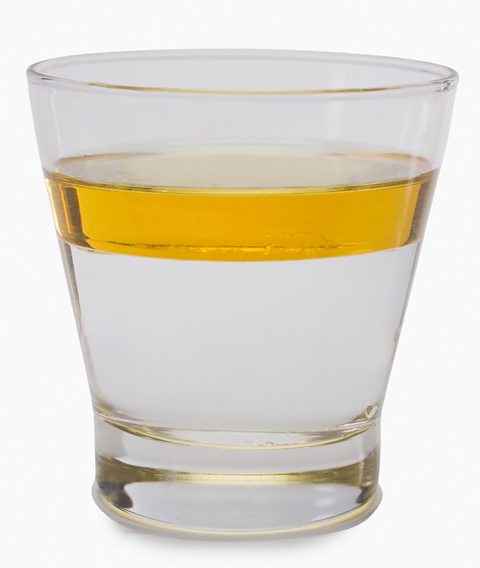

You can make your own experiment to explore the different densities of liquids.
You will need:
- golden syrup
- water
- cooking oil
- a tall jar
Add each liquid slowly and carefully to the jar so that don’t mix.
Which liquid is the most dense? Which liquid is the least dense?

Activity
Buoyancy isn't just about density. Shape makes a difference too as you can find out in this experiment.

Try this floating and sinking experiment!
You will need:
- Tin foil to make boats from
- A container filled with water
- Marbles or coins to act as weights
Make different shapes of boat with the tin foil. See how much weight you can add before they sink.
Watch the video to find out more.
Video
Watch this video to find out what to do!
Key words

Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – How well something floats. If an object can float, we say that it is buoyant.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – How tightly packed the material inside something is. Objects with higher density than water will not float…
Quiz
Test your knowledge of buoyancy with our fun quiz!
More on Forces
Find out more by working through a topic
- count10 of 11

- count11 of 11
- count1 of 11

- count2 of 11